When we talk about any process control, we talk about three elements:
In Scrum, decisions are made based on observation and experimentation rather than on detailed upfront planning. Empirical process control relies on the three main ideas of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
Inspection
Inspection in Scrum is depicted through the following:
- Input
- Process (structured set of activities designed to accomplish a specific objective)
- Output
In Scrum, decisions are made based on observation and experimentation rather than on detailed upfront planning. Empirical process control relies on the three main ideas of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
Transparency
Transparency allows all facets of any Scrum process to be observed by anyone. This promotes an easy and transparent flow of information throughout the organization and creates an open work culture.Inspection
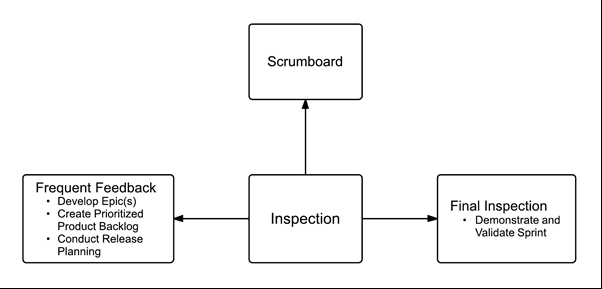
Inspection in Scrum is depicted through the following:
- Use of a common Scrumboard and other information radiators which show the progress of the Scrum Team on completing the tasks in the current Sprint
- Collection of feedback from the customer and other stakeholders during the Develop Epic(s), Create Prioritized Product Backlog , and Conduct Release Planning processes
- Inspection and approval of the Deliverables by the Product Owner and the customer in the Demonstrate and Validate Sprint process.
Adaptation
Adaptation happens as the Scrum Core Team and Stakeholders learn through transparency and inspection and then adapt by making improvements in the work they are doing.
Acknowledgement:
The content is borrowed from www.scrumstudy.com (original blog url: http://www.scrumstudy.com/blog/what-is-empirical-process-control/)



No comments:
Post a Comment